American Academy of Pediatrics and other medical experts exclusively recommend to breastfeed the baby for first 6 months. Once you introduce baby to other foods it is recommended to breastfeed for at least first year of babys life. Taking medication while breastfeeding could be tricky as most drugs pass in breast milk. In this article we will evaluate Lorabid | Loracarbef Capsule for its safety in breastfeeding.
What is Lorabid | Loracarbef Capsule used for?
Lorabid is indicated in the treatment of patients with mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the conditions listed below. (As recommended dosages, durations of therapy, and applicable patient populations vary among these infections, please see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION for specific recommendations.) Lower Respiratory Tract Secondary Bacterial Infection of Acute Bronchitis caused by S. pneumoniae , H. influenzae (including β-lactamase-producing strains), or M. catarrhalis (including β-lactamase-producing strains). Acute Bacterial Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis caused by S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae (including β-lactamase-producing strains), or M. catarrhalis (including β-lactamase-producing strains). Pneumonia caused by S. pneumoniae or H. influenzae (non-β-lactamase-producing strains only). Data are insufficient at this time to establish efficacy in patients with pneumonia caused by β-lactamase-producing strains of H. influenzae. Upper Respiratory Tract Otitis Media † caused by S. pneumonia, H. influenzae (including β-lactamase-producing strains), M. catarrhalis (including β-lactamase-producing strains), or S. pyogenes. Acute Maxillary Sinusitis † caused by S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae (non-β-lactamase-producing strains only), or M. catarrhalis (including β-lactamase-producing strains). Data are insufficient at this time to establish efficacy in patients with acute maxillary sinusitis caused by β-lactamase-producing strains of H. influenzae. † NOTE: In a patient population with significant numbers of β-lactamase-producing organisms, loracarbef's clinical cure and bacteriological eradication rates were somewhat less than those observed with a product containing a β-lactamase inhibtor. Lorabid's decreased potential for toxicity compared to products containing β-lactamase inhibitors along with the susceptibility patterns of the common microbes in a given geographic area should be taken into account when considering the use of an antimicrobial (see CLINICAL STUDIES section). For information on use in pediatric patients, see PRECAUTIONS—Pediatric Use. Pharyngitis and Tonsillitis caused by S. pyogenes. (The usual drug of choice in the treatment and prevention of streptococcal infections, including the prophylaxis of rheumatic fever, is penicillin administered by the intramuscular route. Lorabid is generally effective in the eradication of S. pyogenes from the nasopharynx; however, data establishing the efficacy of Lorabid in the subsequent prevention of rheumatic fever are not available at present.) Skin and Skin Structure Uncomplicated Skin and Skin Structure Infections caused by S. aureus (including penicillinase-producing strains) or S. pyogenes. Abscesses should be surgically drained as clinically indicated. Urinary Tract Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections (cystitis) caused by E.coli or S. saprophyticus*. NOTE: In considering the use of Lorabid in the treatment of cystitis, Lorabid's lower bacterial eradication rates and lower potential for toxicity should be weighed against the increased eradication rates and increased potential for toxicity demonstrated by some other classes of approved agents (see CLINICAL STUDIES section). Uncomplicated Pyelonephritis caused by E. coli. *Although treatment of infections due to this organism in this organ system demonstrated a clinically acceptable overall outcome, efficacy was studied in fewer than 10 infections. Culture and susceptibility testing should be performed when appropriate to determine the causative organism and its susceptibility to loracarbef. Therapy may be started while awaiting the results of these studies. Once these results become available, antimicrobial therapy should be adjusted accordingly. CONTRAINDICATION Lorabid is contraindicated in patients with known allergy to loracarbef or cephalosporin-class antibiotics.
I am breastfeeding mother and I am using Lorabid | Loracarbef Capsule. Can it have any bad effect on my kid? Shall I search for better alternative?
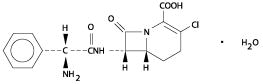
As per our analysis Lorabid | Loracarbef Capsule contains only one ingredient and that is Loracarbef anhydrous. We have analyzed Loracarbef anhydrous and it seems to be safe to use Loracarbef anhydrous while breastfeeding, that means usage of Lorabid | Loracarbef Capsule shall be safe while breastfeeding. Below you can check more details of Loracarbef anhydrous usage in breastfeeding. We recommend you to go through provided detailed analysis as below take decision accordingly.
Statement of Manufacturer/Labeler about breastfeeding usage
Nursing Mothers—It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Lorabid is administered to a nursing woman.
Lorabid | Loracarbef Capsule Breastfeeding Analsys
SafeCAS Number: 76470-66-1
Second-generation cephalosporin for oral administration with a chemical structure similar to cefaclor. At latest update no published data on excretion into breast milk were found. Cephalosporins for which data are available have shown to be excreted into milk in non-significant amount from a therapeutic point of view without reported complications in infants related to them.Cephalosporins are widely used in the Pediatric practice with a high tolerance, even in the neonatal period, so it is very unlikely that such small amounts present in the milk may be a cause of problems to the infant. Be aware of the possibility of false negative results of cultures in febrile infants whose mothers are taking antibiotics as well as the possibility of gastroenteritis (Ito 1993) by altering the intestinal flora.
Lorabid | Loracarbef Capsule Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
CAS Number: 76470-66-1
Although no information is available on the use of loracarbef during breastfeeding, beta-lactam antibiotics are generally not be expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. Occasionally disruption of the infant's gastrointestinal flora, resulting in diarrhea or thrush have been reported with beta-lactams, but these effects have not been adequately evaluated. Loracarbef is acceptable in nursing mothers.
I already used Lorabid | Loracarbef Capsule and meanwhile I breastfed my baby should I be concerned?
As usage of Lorabid | Loracarbef Capsule is mostly safe while breastfeeding hence there should not be any concern. In case of any change in behavior or health of your baby you should inform your health care provider about usage of Lorabid | Loracarbef Capsule else no further action is required.
I am nursing mother and my doctor has suggested me to use Lorabid | Loracarbef Capsule, is it safe?
Definitely, Lorabid | Loracarbef Capsule is safe in lactation for baby. No wonder your doctor has recommended it.
If I am using Lorabid | Loracarbef Capsule, will my baby need extra monitoring?
No extra baby monitoring required while mother is using Lorabid | Loracarbef Capsule
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Lorabid | Loracarbef Capsule in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week