Do you know that important immune protective proteins are present in breast milk? Breast milk also contains required vitamins, minerals, saturated and un saturated fats. These things are extremely important for development of healthy brain. If you are taking any medicine for short term or for the chronic reason then that passes in breast milk as well, that is why you should always check the drug with your health care provider. Here at DrLact we try to analyze drugs based on available researches and in this sheet we will present our analysis for Fenofibrate Tablet.
What is Fenofibrate Tablet used for?
Treatment of Hypercholesterolemia Fenofibrate tablets, USP are indicated as adjunctive therapy to diet to reduce elevated LDL-C, Total-C, Triglycerides and Apo B, and to increase HDL-C in adult patients with primary hypercholesterolemia or mixed dyslipidemia (Fredrickson Types IIa and IIb). Lipid-altering agents should be used in addition to a diet restricted in saturated fat and cholesterol when response to diet and non-pharmacological interventions alone has been inadequate (See National Cholesterol Education Program [NCEP] Treatment Guidelines, below). Treatment of Hypertriglyceridemia Fenofibrate tablets, USP are also indicated as adjunctive therapy to diet for treatment of adult patients with hypertriglyceridemia (Fredrickson Types IV and V hyperlipidemia). Improving glycemic control in diabetic patients showing fasting chylomicronemia will usually reduce fasting triglycerides and eliminate chylomicronemia thereby obviating the need for pharmacologic intervention. Markedly elevated levels of serum triglycerides (e.g. > 2,000 mg/dL) may increase the risk of developing pancreatitis. The effect of fenofibrate tablet, USP therapy on reducing this risk has not been adequately studied. Drug therapy is not indicated for patients with Type I hyperlipoproteinemia, who have elevations of chylomicrons and plasma triglycerides, but who have normal levels of very low density lipoprotein (VLDL). Inspection of plasma refrigerated for 14 hours is helpful in distinguishing Types I, IV and V hyperlipoproteinemia 2. The initial treatment for dyslipidemia is dietary therapy specific for the type of lipoprotein abnormality. Excess body weight and excess alcoholic intake may be important factors in hypertriglyceridemia and should be addressed prior to any drug therapy. Physical exercise can be an important ancillary measure. Diseases contributory to hyperlipidemia, such as hypothyroidism or diabetes mellitus should be looked for and adequately treated. Estrogen therapy, thiazide diuretics and beta-blockers, are sometimes associated with massive rises in plasma triglycerides, especially in subjects with familial hypertriglyceridemia. In such cases, discontinuation of the specific etiologic agent may obviate the need for specific drug therapy of hypertriglyceridemia. The use of drugs should be considered only when reasonable attempts have been made to obtain satisfactory results with non-drug methods. If the decision is made to use drugs, the patient should be instructed that this does not reduce the importance of adhering to diet. (See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS). Fredrickson Classification of Hyperlipoproteinemias C = cholesterol TG = triglycerides LDL = low density lipoprotein VLDL = very low density lipoprotein IDL = intermediate density lipoprotein Lipid Elevation Type Lipoprotein Elevated Major Minor I (rare) chylomicrons TG ↑↔C IIa LDL C - IIb LDL, VLDL C TG III (rare) IDL C, TG - IV VLDL TG ↑↔C V (rare) chylomicrons, VLDL TG ↑↔ NCEP Treatment Guidelines: LDL-C Goals and Cutpoints for Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes and Drug Therapy in Different Risk Categories †CHD = coronary heart disease ††Some authorities recommend use of LDL-lowering drugs in this category if an LDL-C level of < 100 mg/dL cannot be achieved by therapeutic lifestyle changes. Others prefer use of drugs that primarily modify triglycerides and HDL-C, e.g., nicotinic acid or fibrate. Clinical judgment also may call for deferring drug therapy in this subcategory. †††Almost all people with 0 to 1 risk factor have 10-year risk < 10%; thus, 10-year risk assessment in people with 0 to 1 risk factor is not necessary. Risk Category LDL Goal (mg/dL) LDL Level at Which to Initiate Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes (mg/dL) LDL Level at Which to Consider Drug Therapy (mg/dL) CHD † or CHD risk equivalents (10-years risk > 20%) < 100 ≥ 100 ≥ 130 (100 to 129: drug optional) †† 2+ Risk Factors (10-year risk ≤ 20%) < 130 ≥ 130 10-year risk 10% to 20%: ≥ 130 10-year risk < 10%: ≥ 160 0 to 1 Risk Factor ††† < 160 ≥ 160 ≥ 190 (160 to 189: LDL- lowering drug optional) After the LDL-C goal has been achieved, if the TG is still ≥ 200 mg/dL, non HDL-C (total-C minus HDL-C) becomes a secondary target of therapy. Non-HDL-C goals are set 30 mg/dL higher than LDL-C goals for each risk category.
Is Fenofibrate Tablet usage safe while breastfeeding? If a lactating mother is using it can there be any effect on growth or development of infant?
Fenofibrate Tablet contains only one active ingredient that is Fenofibrate. We have analyzed the usage of Fenofibrate in breastfeeding and our analysis suggest that Fenofibrate poses Low risk for infant while breastfeeding and hence Fenofibrate Tablet itself shall be considered Low risk item for breastfeeding.
Statement of Manufacturer/Labeler about breastfeeding usage
Nursing Mothers Fenofibrate should not be used in nursing mothers. Because of the potential for tumorigenicity seen in animal studies, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug.
Fenofibrate Tablet Breastfeeding Analsys
Low RiskCAS Number: 49562-28-9
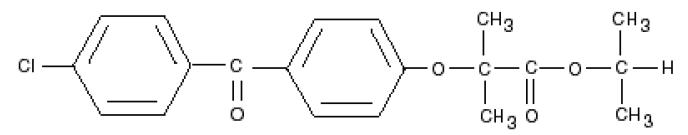
Fenofibrate, like other fibrates, decreases elevated blood lipids (triglycerides and cholesterol) by increasing the activity of lipases that catabolize triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and slightly decreasing cholesterol biosynthesis (AEMPS 2017, BGP 2015, Miller 1998). In general, fibrates have a discrete effect on the increase of high density lipoprotein (HDL) concentration and the reduction of low density lipoprotein (LDL). Since the last update we have not found published data in relation to breastfeeding. Its high binding to plasma proteins makes it unlikely it will pass into breast milk. Cholesterol levels in milk are very stable even in hypercholesterolemic women and are not severely affected by diet or nutritional status of the mother, suggesting that 3 is synthesized, at least in part, in the mammary gland (Lawrence 2016, p 289-90).It is not probable therefore, but it is not known if the fibrates are able to alter the lipid composition of the milk. Infants need to ingest large amounts of cholesterol, as it is critical to the proper development of the nervous system, cell membranes and is a precursor of several hormones and vitamins. Until there is more data in relation to breastfeeding, it is prudent to avoid using it, at least while breastfeeding exclusively. Suspending the pharmacological treatment of hyperlipidemia during breastfeeding is not likely to alter the long-term outcome of the disease, especially when breastfeeding can be considered therapeutic (Lawrence 2016, p.393). It is advisable to follow a lipid-lowering diet. In case of administering a fibrate during breastfeeding it is advisable to choose those with a shorter half-life: bezafibrate, gemfibrozil.
Fenofibrate Tablet Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
CAS Number: 49562-28-9
No relevant published information exists on the use of fenofibrate during breastfeeding. Because of a concern with disruption of infant lipid metabolism, fenofibrate is best avoided during breastfeeding. An alternate drug is preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be avoided during fenofibrate therapy and for 5 days after the final dose.
I already used Fenofibrate Tablet and meanwhile I breastfed my baby should I be concerned?
Fenofibrate Tablet is in the category of low risk, if you have already used it then its not a big deal if health and behavior of baby is good. However your health care provider shall be aware of the fact that you have used Fenofibrate Tablet so you should inform him based on your convenience.
I am nursing mother and my doctor has suggested me to use Fenofibrate Tablet, is it safe?
Fenofibrate Tablet comes in category of low risk and if your doctor is aware that you are breastfeeding it should be ok to use without much concerns.
If I am using Fenofibrate Tablet, will my baby need extra monitoring?
Not much monitoring required while using Fenofibrate Tablet
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Fenofibrate Tablet in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Drug Brands with same Active ingredients



