Indapamide Indapamide 1.0 Mg while Breastfeeding
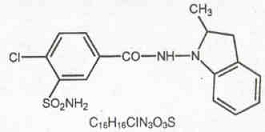
What is Indapamide Indapamide 1.0 Mg used for?
Usage in Pregnancy: The routine use of diuretics in an otherwise healthy woman is inappropriate and exposes mother and fetus to unnecessary hazard (see PRECAUTIONS). Diuretics do not prevent development of toxemia of pregnancy, and there is no satisfactory evidence that they are useful in the treatment of developed toxemia. Edema during pregnancy may arise from pathological causes or from the physiologic and mechanical consequences of pregnancy. Indapamide is indicated in pregnancy when edema is due to pathologic causes, just as it is in the absence of pregnancy (however, see PRECAUTIONS). Dependent edema in pregnancy, resulting from restriction of venous return by the expanded uterus, is properly treated through elevation of the lower extremities and use of support hose; use of diuretics to lower intravascular volume in this case is illogical and unnecessary. There is hypervolemia during normal pregnancy which is not harmful to either the fetus or the mother (in the absence of cardiovascular disease), but which is associated with edema, including generalized edema in the majority of pregnant women. If this edema produces discomfort, increased recumbency will often provide relief. In rare instances, this edema may cause extreme discomfort which is not relieved by rest. In these cases, a short course of diuretics may provide relief and may be appropriate.
I am breastfeeding mother and I am using Indapamide Indapamide 1.0 Mg. Can it have any bad effect on my kid? Shall I search for better alternative?

Nursing Mothers: It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because most drugs are excreted in human milk, if use of this drug is deemed essential, the patient should stop nursing.
Indapamide Indapamide 1.0 Mg Breastfeeding Analsys
Indapamide while Breastfeeding
Low RiskCAS Number: 26807-65-8
Thiazide-like diuretic. Long-term treatment with diuretic drugs (particularly those Thiazides with long lasting effect and loop-acting drugs) may inhibit lactation. Use a lower dose as possible, especially during the first postnatal month.
Indapamide Indapamide 1.0 Mg Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
Indapamide while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 26807-65-8
If indapamide is required by the mother, it is not a reason to discontinue breastfeeding. Intense diuresis with large doses may decrease breastmilk production.
I already used Indapamide Indapamide 1.0 Mg and meanwhile I breastfed my baby should I be concerned?
Indapamide Indapamide 1.0 Mg is in the category of low risk, if you have already used it then its not a big deal if health and behavior of baby is good. However your health care provider shall be aware of the fact that you have used Indapamide Indapamide 1.0 Mg so you should inform him based on your convenience.
I am nursing mother and my doctor has suggested me to use Indapamide Indapamide 1.0 Mg, is it safe?
Though Indapamide Indapamide 1.0 Mg dose not comes in category of safe drugs rather it comes in category of low risk but if your doctor is aware that you are breastfeeding your baby and has still recommended it then its advantages must be outweighing the risks.
If I am using Indapamide Indapamide 1.0 Mg, will my baby need extra monitoring?
Not much monitoring required while using Indapamide Indapamide 1.0 Mg
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Indapamide Indapamide 1.0 Mg in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
