4342 First Aid Kit Kit while Breastfeeding

What is 4342 First Aid Kit Kit used for?
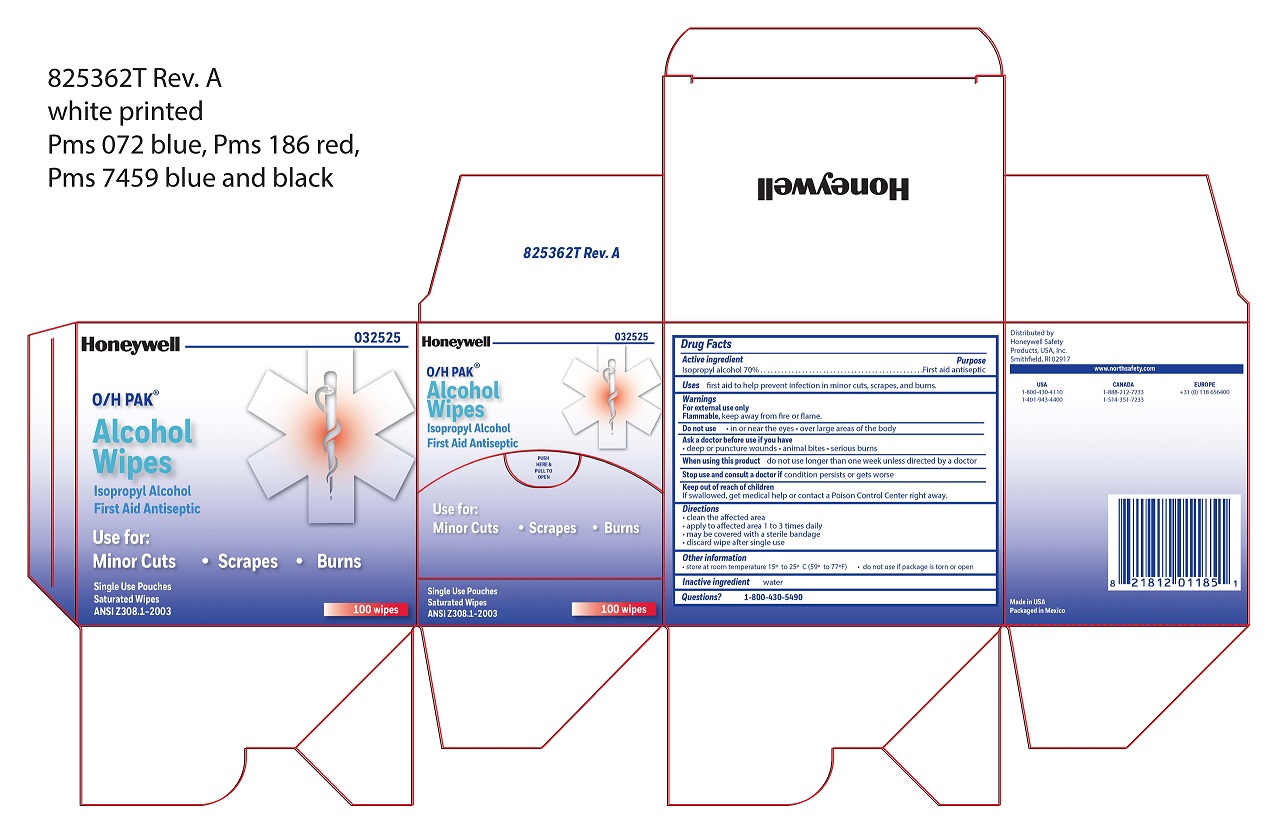
Aspirin Uses temporarily reduces fever and relieves minor aches and pains associated with: a cold headache toothache muscular aches backache minor pain of arthritis premenstrual and menstrual periods
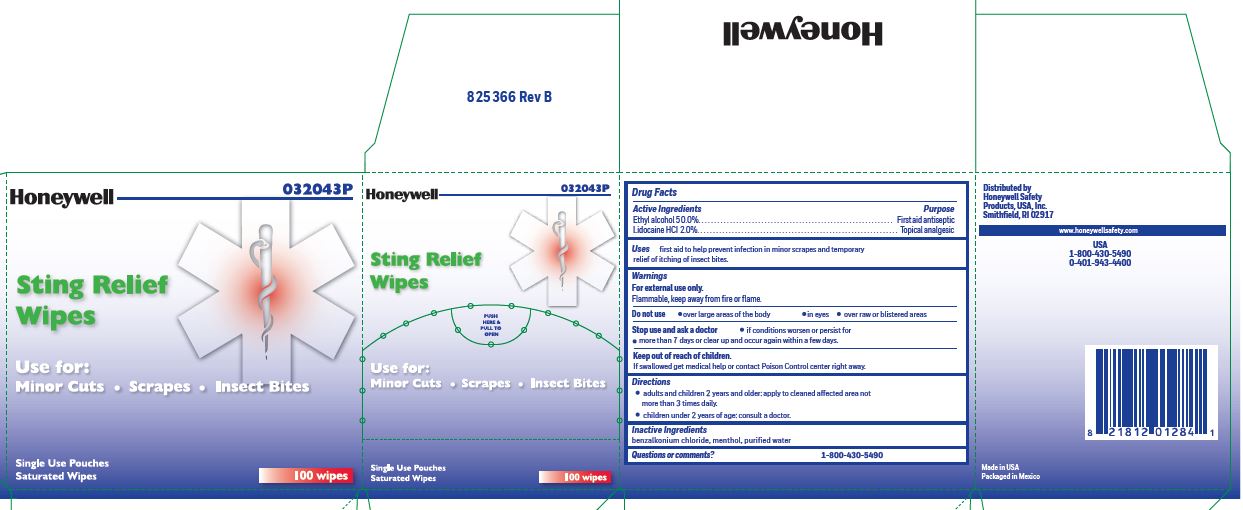
Sting Relief Uses prevent infection in minor scrapes, and temporary relief of itching of insect bites
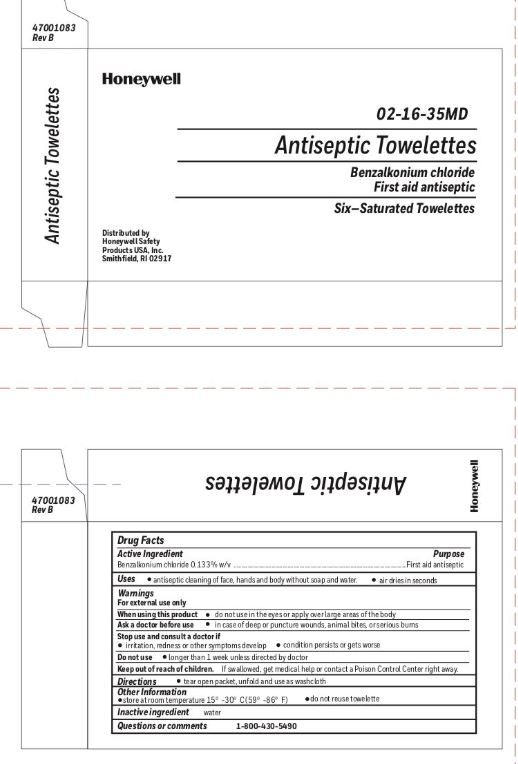
BZK Uses Antiseptic cleansing of face, hands, and body without soap and water
Neomycin Uses first aid to help prevent infection in minor cuts scrapes burns Do not use in the eyes over large areas of the body
Aypanal EX Uses temporarily relieves minor aches and pains due to the common cold and headache - temporarily reduces fever
Purpose: Alcohol Wipe Purpose First aid antiseptic
Aspirin Purpose Pain reliever/fever reducer
Sting Relief Purpose Antiseptic Topical pain relief
BZK Purpose First aid antiseptic
Neomycin Purpose First aid antibiotic
Aypanal EX PUrpose Pain reliever/fever reducer
Is 4342 First Aid Kit Kit usage safe while breastfeeding? If a lactating mother is using it can there be any effect on growth or development of infant?

4342 First Aid Kit Kit Breastfeeding Analsys
Acetaminophen while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 103-90-2
Excreted in very low amount into breast milk. Infant intake may be lower than 4% of usual pediatric dose. The American Academy of Pediatrics rates it as compatible with Breastfeeding.
Aspirin while Breastfeeding
Low RiskCAS Number: 50-78-2
Excreted in non-significant amount into breast milk. Reye’s Syndrome has never been reported due to ASA through breast milk. It is thought to be highly unlikely to occur after isolated or small doses like those used for treatment of thrombosis or anti-abortion therapy. At high maternal dose, one case (dubious) of salicylic intoxication in the neonatal period and another case of thrombocytopenia in an infant have been reported. Likelihood of hemolysis should be considered in those patients with G6PD-deficiency. WHO Model List of Essential Medication: compatible while breastfeeding when used occasionally or small dose for antithrombotic prophylaxis management.
Neomycin sulfate while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 1404-04-2
Aminoglycoside antibiotic which is used in creams, eye drops, and otologic preparations for topical use, and, also orally used for intestinal disinfection. At latest update, relevant published data on excretion in the breast milk were not found. Like other aminoglycoside antibiotics, Neomycin is not absorbed by the gut. Absorption from other sources like skin, nose, ear and eye mucosa by means of topically used preparations (creams, drops, etc.) is very poor which causes excretion into breast milk in significant amount, unlikely. Do not apply creams, gels and other products that would contain paraffin (mineral oil) to avoid absorption by the infant since it is a hydrocarbon-derived substance. In case of use of Neomycin on the nipple, let it be done after the feed and wipe it out any excess of cream before the next feed. Be aware of false negative results of microbial cultures done from samples of febrile infants whose mothers are treated with antibiotics. Also, due to imbalance of intestinal flora a diarrheal disease can occur in the breastfed infant. List of Essential Medicines by WHO 2002: compatible with breastfeeding.
Lidocaine hydrochloride anhydrous while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 137-58-6
Compatible with breastfeeding no matter the multiple ways it can be used: anesthetic, anti-arrhythmic, or anti-epileptic drug. Excreted into breast milk in non-significant amount with no side effects on breastfed infants from treated mothers. As a topical anesthetic (dermatologic, dental-stomatologic, ophtalmotologic and otologic preparations) it has an almost nil systemic absorption. Avoid using it on the nipple, but if necessary do it after the breast feed, wipe it out and rinse with water before the next feed, An euptectic mixture with added Prilocaine (EMLA) is used for dermatologic anesthesia. There is an increased risk of Methemoglobinemia when applied on large surfaces or taken by mouth. Intrapartum anesthesia may delay the onset of phase II of Lactogenesis or milk coming-in. The American Academy of Pediatrics rates it usually compatible with Breastfeeding.
4342 First Aid Kit Kit Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
Acetaminophen while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 103-90-2
Acetaminophen is a good choice for analgesia, and fever reduction in nursing mothers. Amounts in milk are much less than doses usually given to infants. Adverse effects in breastfed infants appear to be rare.
Aspirin while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 50-78-2

After aspirin ingestion, salicylic acid is excreted into breastmilk, with higher doses resulting in disproportionately higher milk levels. Long-term, high-dose maternal aspirin ingestion probably caused metabolic acidosis in one breastfed infant. Reye's syndrome is associated with aspirin administration to infants with viral infections, but the risk of Reye's syndrome from salicylate in breastmilk is unknown. An alternate drug is preferred over continuous high-dose, aspirin therapy. After daily low-dose aspiring (75 to 325 mg daily), no aspirin is excreted into breastmilk and salicylate levels are low. Daily low-dose aspirin therapy may be considered as an antiplatelet drug for use in breastfeeding women.[1][2][3].
Neomycin sulfate while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 1404-04-2
Although no information exists on the excretion of neomycin into milk, other aminoglycoside antibiotics are poorly excreted into breastmilk. Newborn infants apparently absorb small amounts of aminoglycosides, but serum levels are far below those attained when treating newborn infections and systemic effects of neomycin are unlikely. Older infants would be expected to absorb even less neomycin. Monitor the infant for possible effects on the gastrointestinal flora, such as diarrhea, candidiasis (e.g., thrush, diaper rash) or rarely, blood in the stool indicating possible antibiotic-associated colitis. Oral, topical, ophthalmic or otic neomycin should result in very low levels in breastmilk and present negligible risk to the infant,[1][2] although topical application to the nipple may increase the risk of diarrhea in the infant. Only water-miscible cream or gel products should be applied to the breast because ointments may expose the infant to high levels of mineral paraffins via licking.[3]
Benzalkonium chloride while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 8001-54-5
Topical maternal application of benzalkonium chloride or benzethonium chloride or their presence as a preservative in pharmaceuticals would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants.
Lidocaine hydrochloride anhydrous while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 137-58-6
Lidocaine concentrations in milk during continuous IV infusion, epidural administration and in high doses as a local anesthetic are low and the lidocaine is poorly absorbed by the infant. Lidocaine is not expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. No special precautions are required.[1][2][3] Lidocaine labor and delivery with other anesthetics and analgesics has been reported by some to interfere with breastfeeding. However, this assessment is controversial and complex because of the many different combinations of drugs, dosages and patient populations studied as well as the variety of techniques used and deficient design of many of the studies. Overall it appears that with good breastfeeding support epidural lidocaine with or without fentanyl or one of its derivatives has little or no adverse effect on breastfeeding success.[4][5][6][7][8] Labor pain medication may delay the onset of lactation.
4342 First Aid Kit Kit Breastfeeding Analsys - 3
Isopropyl alcohol and Breastfeeding
SafeIsopropyl alcohol is used as rubbing alcohol. Topically, it is used as an antiseptic. Some recent studies suggest dermal absorption of Isopropyl alcohol however its presence in breast milk is unknown. Normal usage of Isopropyl alcohol as rubbing alcohol is likely safe in lactation.
Note: Study and data for tropical use onlyWarning: Tropical usage in breast area shall be avoided
Benzalkonium chloride and Breastfeeding
SafeNote: Study and data for tropical use only
Alcohol and Breastfeeding
SafePregnant and breast-feeding healthcare workers appear to be well within safe exposure limits and can use alcohol-based hand rubs and similar products without risk to fetus or baby. The internal doses of ethanol associated with frequent use of hand sanitizers and scrubs are hundreds of times lower than the concentration that might be related to developmental effects.
Note: Study and data for tropical use onlyWarning: Tropical usage in breast area shall be avoided to prevent it passing orally in Infants.
I am nursing mother and I have already used 4342 First Aid Kit Kit, what should I do?
It is always a good idea to keep your healthcare provider or doctor informed about your drug usage during pregnancy and breastfeeding but if you have not informed your doctor about 4342 First Aid Kit Kit and have used it then do not panic as 4342 First Aid Kit Kit is mostly safe in breastfeeding and should not cause any harm to your baby.
I am nursing mother and my doctor has suggested me to use 4342 First Aid Kit Kit, is it safe?
Usage of 4342 First Aid Kit Kit is safe for nursing mothers and baby, No worries.
If I am using 4342 First Aid Kit Kit, will my baby need extra monitoring?
No
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of 4342 First Aid Kit Kit in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
