Lamotrigine | Cardinal Health while Breastfeeding

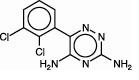
What is Lamotrigine | Cardinal Health used for?
I am breastfeeding mother and I am using Lamotrigine | Cardinal Health. Can it have any bad effect on my kid? Shall I search for better alternative?

8.3. Nursing Mothers Lamotrigine is present in milk from lactating women taking lamotrigine tablets. Data from multiple small studies indicate that lamotrigine plasma levels in human milk-fed infants have been reported to be as high as 50% of the maternal serum levels. Neonates and young infants are at risk for high serum levels because maternal serum and milk levels can rise to high levels postpartum if lamotrigine dosage has been increased during pregnancy but not later reduced to the pre-pregnancy dosage. Lamotrigine exposure is further increased due to the immaturity of the infant glucuronidation capacity needed for drug clearance. Events including apnea, drowsiness, and poor sucking have been reported in infants who have been human milk-fed by mothers using lamotrigine; whether or not these events were caused by lamotrigine is unknown. Human milk-fed infants should be closely monitored for adverse events resulting from lamotrigine. Measurement of infant serum levels should be performed to rule out toxicity if concerns arise. Human milk-feeding should be discontinued in infants with lamotrigine toxicity. Caution should be exercised when lamotrigine tablets is administered to a nursing woman.
Lamotrigine | Cardinal Health Breastfeeding Analsys
Lamotrigine while Breastfeeding
Low RiskCAS Number: 84057-84-1
As high as therapeutic levels of this drug have been found in the serum of infants (35-50% of maternal serum level). Side-effects were not observed, neither developmental nor IC derangements at long term follow-up among hundreds of children of treated mothers. A case was published of apnea in a newborn baby whose mother was on a very high dose of Lamotrigine (850 mg a-day). During pregnancy, it increases the clearance of Lamotrigine and other antiepileptic medication that warrants an increase in dosage in this period. After birth, the serum level rapidly increases with a risk of harm on both the mother and the infant, whenever dose is not reduced to that previous from pregnancy. An infant, 1 1/2 months old, whose mother was on Lamotrigine, resulted affected with Abstinence Syndrome soon after sudden weaning.
Lamotrigine | Cardinal Health Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
Lamotrigine while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 84057-84-1
Occasional adverse reactions have been reported in infants who receive lamotrigine in milk, but long-term exposure does not appear to affect infant growth and development. Breastfed infants whose mothers are taking lamotrigine have relatively high plasma lamotrigine levels. Neonates are particularly at risk for high plasma levels because their ability to metabolize the drug by glucuronidation is limited, plasma protein binding is relatively low, and maternal plasma and milk levels can rise dramatically in the immediate postpartum period if the dosage is not reduced to the prepregnancy dosage.[1][2] If lamotrigine is required by the mother, it is not necessarily a reason to discontinue breastfeeding, because many infants have been breastfed without adverse reactions. However, breastfed infants should be carefully monitored for side effects such as apnea, rash, drowsiness or poor sucking, including measurement of serum levels to rule out toxicity if there is a concern. Monitoring of the platelet count and liver function may also be advisable. If an infant rash occurs, breastfeeding should be discontinued until the cause can be established.
I already used Lamotrigine | Cardinal Health and meanwhile I breastfed my baby should I be concerned?
Lamotrigine | Cardinal Health is in the category of low risk, if you have already used it then its not a big deal if health and behavior of baby is good. However your health care provider shall be aware of the fact that you have used Lamotrigine | Cardinal Health so you should inform him based on your convenience.
I am nursing mother and my doctor has suggested me to use Lamotrigine | Cardinal Health, is it safe?
Lamotrigine | Cardinal Health comes in category of low risk and if your doctor is aware that you are breastfeeding it should be ok to use
If I am using Lamotrigine | Cardinal Health, will my baby need extra monitoring?
Not much monitoring required while using Lamotrigine | Cardinal Health
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Lamotrigine | Cardinal Health in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
