Proscenat while Breastfeeding
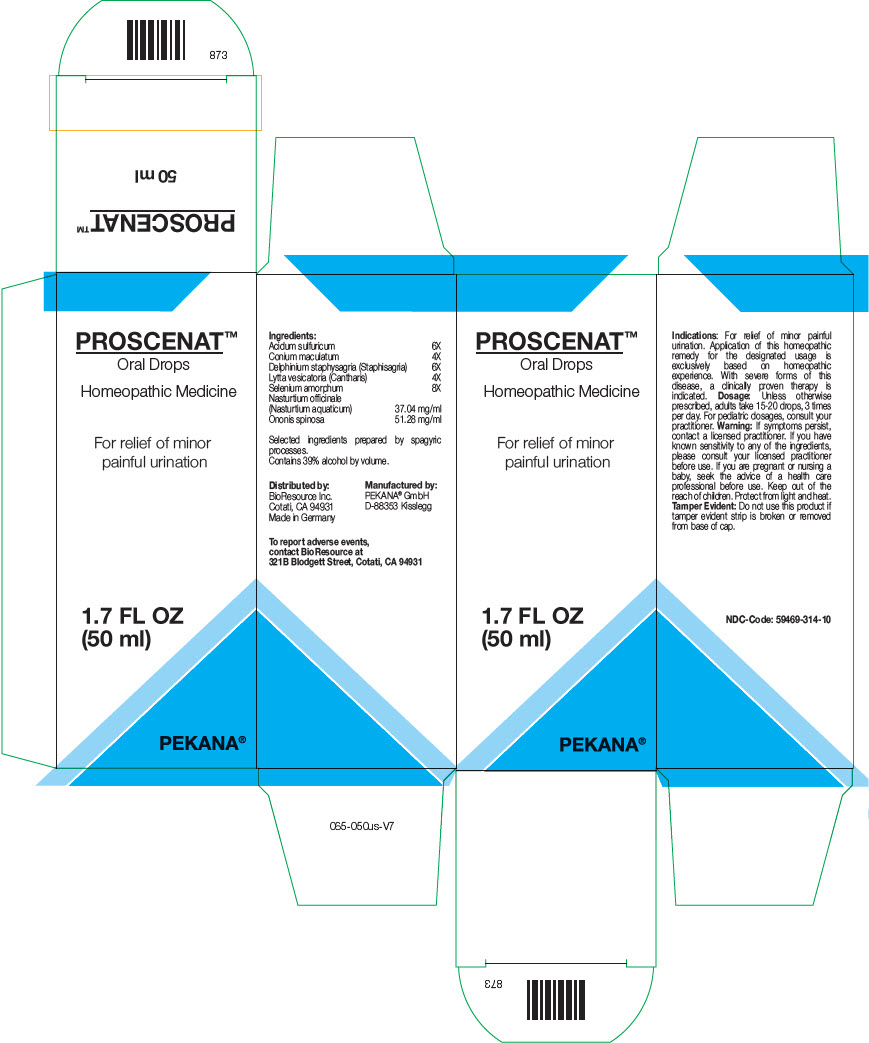
What is Proscenat used for?
Purpose: For relief of minor painful urination. Application of this homeopathic remedy for the designated usage is exclusively based on homeopathic experience. With severe forms of this disease, a clinically proven therapy is indicated.
Is Proscenat usage safe while breastfeeding? If a lactating mother is using it can there be any effect on growth or development of infant?

Proscenat Breastfeeding Analsys
Selenium while Breastfeeding
Low RiskCAS Number: 7782-49-2
Essential trace element necessary for the functioning of the glutathione-peroxidase enzyme system that protects cellular structures from oxidative damage. It is obtained from foods such as vegetables, cereals, legumes, garlic, fish, seafood, eggs and meat. The amount of selenium in these sources depends on the concentration of selenium in the soil. The brazil nut (Bertholletia excelsa) is the food with the highest known concentrations of selenium. Selenium deficiency is very rare. With a staple diet it is not necessary to take selenium supplements in the absence of disease or a condition that may warrant it: parenteral nutrition, Crohn's disease, prematurity (MedlinePlus 2017). Taking too much selenium can cause selenosis, a condition that causes dermatological symptoms (alopecia, nail dystrophy), digestive symptoms, neurological symptoms and fatigue (MedlinePlus 2017).Nutritional supplements containing excessive amounts of selenium have resulted in severe poisoning (Aldosary 2012, Senthilkumaran 2012).The potential effects of selenium on cancer prevention, cardiovascular disease, and heavy metal poisoning and toxins are not proven, so supplementation of selenium other than from normal diet is not recommended (MedlinePlus 2017). The daily needs of selenium for breastfeeding mothers are 70-75 micrograms (mcg) daily. In infants it is 2 to 3 mcg/kg (10 mcg/day during the first 4 months) with a maximum of 30 mcg/day (MedlinePlus 2017, Kipp 2015). Selenium is found naturally in milk in its organic form of selenomethionine (Dorea 2002). The amount of selenium in colostrum is 80 mcg per litre and in mature milk 12-20 mcg/L, with no or very weak correlation with plasma selenium levels or daily intake of selenium (Wasowicz 2001, Bianchi 1999, Artaud 1993, Cummings 1992, Levander 1987, Higashi 1983). However, there are authors who find that selenium supplements for breastfeeding mothers increase selenium levels in milk and infants may exceed their daily needs for selenium. (Dorea 2002, Trafikowska 1996). Better plasma levels of selenium have been found in breastfed infants than in formula-fed infants (Strambi 2004, Sorvacheva 1996). There are lower plasma levels of selenium in babies born small for their gestational age (Strambi 2004).
Proscenat Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
Conium maculatum flowering top and Breastfeeding
UnsafeHemlock is a very poisonous plant. In fact, all parts of the plant are toxic. Hemlock is most poisonous during the early stages of growth in the spring, but it is dangerous at all stages of growth. The poisons in hemlock are so deadly that people have died after eating animals that had eaten hemlock parts.
Despite serious safety concerns, hemlock is used for bronchitis, whooping cough, asthma, arthritis, and other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses. Due to extreme dilution it could be safe in homeopathic medicine however not much study has been done hence shall be avoided.
What should I do if already breastfed my kid after using Proscenat?
Due to high dilution of ingredients in homeopathic medicines they do not create much problem for baby. Proscenat is a homeopathic medicine and if your baby does not have any abnormal symptoms then there is nothing to worry about. Be careful with too much usage of ethanol based homeopathic medicines during breastfeeding.
I am nursing mother and my doctor has suggested me to use Proscenat, is it safe?
Homeopathic medicines are usually safe in breastfeeding and if Proscenat has been recommended by doctor then there should be no concern about its usage in breastfeeding.
If I am using Proscenat, will my baby need extra monitoring?
Not exactly.
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Proscenat in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
