
Carisoprodol, Aspirin And Codeine Phosphate Tablet while Breastfeeding
What is Carisoprodol, Aspirin And Codeine Phosphate Tablet used for?
Is using Carisoprodol, Aspirin And Codeine Phosphate Tablet unsafe in breastfeeding? Can there be bad consequences for baby if I use it while breastfeeding?

Nursing Mothers Carisoprodol is excreted in human milk in concentrations two-to-four times that in maternal plasma. Aspirin is excreted in human milk in moderate amounts and can produce a bleeding tendency in nursing infants. Because of the potential for serious adverse reaction in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Carisoprodol, Aspirin And Codeine Phosphate Tablet Breastfeeding Analsys
Carisoprodol while Breastfeeding
Low RiskCAS Number: 78-44-4
Skeletal muscle relaxant with sedative effects on the central nervous system. It is metabolized to meprobamate.Indicated on low back pain. It is excreted into breast milk in a clinically non-significant amount (Nordeng 2001, Bailey 2002, Briggs 2008) without problems being observed on infants whose mothers were receiving this medication, (Nordeng 2001), except for a mild sedation with higher maternal drug doses (Briggs 2008) .Plasma levels in the infant were undetectable (Briggs 2008). Carisoprodol use increases the risk of abuse and addictive behavior, intoxication and possible psychomotor impairment (Bailey 2002, EMA 2007) being such a reason to be withdrawn from the market in some countries. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has recommended to withhold authorizations for marketing of medicines that contains Carisoprodol (EMA 2007, Reeves 2012, Bramases 2012). If administered during breastfeeding, it is advisable to use a minimum effective dose and monitor a possible sedation on the infant and an inadequate milk production (Sachs 2013).
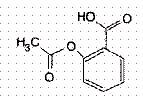
Aspirin while Breastfeeding
Low RiskCAS Number: 50-78-2
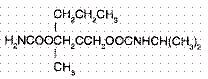
Excreted in non-significant amount into breast milk. Reye’s Syndrome has never been reported due to ASA through breast milk. It is thought to be highly unlikely to occur after isolated or small doses like those used for treatment of thrombosis or anti-abortion therapy. At high maternal dose, one case (dubious) of salicylic intoxication in the neonatal period and another case of thrombocytopenia in an infant have been reported. Likelihood of hemolysis should be considered in those patients with G6PD-deficiency. WHO Model List of Essential Medication: compatible while breastfeeding when used occasionally or small dose for antithrombotic prophylaxis management.
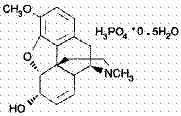
Codeine phosphate while Breastfeeding
UnsafeCAS Number: 76-57-3
Compound of cough and pain medication. The cytochrome P450-CYP2D6 enzyme catalyzes morphine. It is excreted in breast milk in small amounts, much lower than the dose used for newborns and infants. The plasma levels of infants whose mothers take them are very low, less than usual therapeutic levels and assuming an insignificant relative dose, less than 1.5% (Meny 1993, Naumburg 1988, Findlay 1981), so it was considered safe for use during breastfeeding (Bar-Oz 2003, WHO 2002, AAP 2001, Moretti 2000, Spigset 2000, Mitchell 1999, Meny 1993). However, excessive sedation in the mother or infant may occur if they are rapid metabolizers of codeine to morphine due to an excess of the gene linked to the P450-2D6 enzyme: this occurs in <1% of Chinese, Japanese and Hispanic people; 3% African Americans; 1-10% of Caucasians and 16-29% of North Africans, Ethiopians and Saudis (Halder 2015, Sachs 2013). The genetic diagnosis of this characteristic is not available in usual clinical practice (Madadi, 2011). Codeine through breast milk has been linked to the appearance of neonatal apnea (Naumburg, 1988), drowsiness (Ito, 1993), neurological depression (Madadi, 2008) and, above all, a fatal outcome: a newborn whose mother had this genetic abnormality died at 13 days; the mother was taking 60 mg of codeine twice daily, morphine levels were normal in breast milk, but very high in the child's plasma (Madadi 2007, Koren 2006). Subsequently, the causality of codeine in this case has been called into question (Bateman 2008, Ferner RE 2008, Young 2007). A link has been found between the use of codeine during pregnancy and breastfeeding and the risk of developing neuroblastoma in the infant (Cook, 2004). Because of all this, and with newborns having a limited capacity for opioid elimination (Willmann, 2009) and the existence of more effective alternatives, many authors and institutions advocate completely discouraging its use in infants and breastfeeding mothers (FDA 2017, Al-Adhami 2016, Lazaryan 2015, AEMPS 2015, Sachs 2013, EMA 2013). Other authors advocate cautious use (some even in the case of rapid metabolizers), using the lowest possible effective dose and for no more than 4 days and monitoring for signs of sedation in mother and infant (Royal Berkshire-NHS 2016, Halder 2015, Reece-Stremtan-ABM Protocol#21 2015, Chow 2015, Kelly 2013, UKMi NHS 2013, Rowe 2013, Montgomery-ABM protocol#15 2012, Amir 2011, Madadi 2009, Madadi 2007, FDA 2007). The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) better controls pain and with fewer side effects than codeine alone or in combination with paracetamol (Palanisamy 2014, Hendrickson 2012, van den Anker 2012, Madadi 2009, Nauta 2009, Willmann 2009), and codeine is not included either in international consensus on the treatment of migraines (Bordini 2016, Worthington 2013). Follow WHO standards for childbirth attendance, reduce cesarean sections and episiotomies, and therefore the need for analgesics in the first few days.
Carisoprodol, Aspirin And Codeine Phosphate Tablet Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
Carisoprodol while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 78-44-4
If carisoprodol is required by the mother, it is not necessarily a reason to discontinue breastfeeding. Slight sedation has occurred in a breastfed newborn infant who was exposed during pregnancy and lactation; sedation might be more pronounced in newborns who are exposed for the first time during nursing. Other agents may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant, or when other drugs that can cause sedation are used simultaneously.
Aspirin while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 50-78-2
After aspirin ingestion, salicylic acid is excreted into breastmilk, with higher doses resulting in disproportionately higher milk levels. Long-term, high-dose maternal aspirin ingestion probably caused metabolic acidosis in one breastfed infant. Reye's syndrome is associated with aspirin administration to infants with viral infections, but the risk of Reye's syndrome from salicylate in breastmilk is unknown. An alternate drug is preferred over continuous high-dose, aspirin therapy. After daily low-dose aspiring (75 to 325 mg daily), no aspirin is excreted into breastmilk and salicylate levels are low. Daily low-dose aspirin therapy may be considered as an antiplatelet drug for use in breastfeeding women.[1][2][3].
Codeine phosphate while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 76-57-3
Maternal use of codeine during breastfeeding can cause infant drowsiness, central nervous system depression and even death, with pharmacogenetics possibly playing a role.[1][2] Newborn infants seem to be particularly sensitive to the effects of even small dosages of narcotic analgesics. Once the mother's milk comes in, it is best to provide pain control with a nonnarcotic analgesic and limit maternal intake of oral codeine to 2-4 days at a low dosage with close infant monitoring, especially in the outpatient setting.[2][3][4][5] If the baby shows signs of increased sleepiness (more than usual), difficulty breastfeeding, breathing difficulties, or limpness, a physician should be contacted immediately.[6] Excessive sedation in the mother often correlates with excess sedation in the breastfed infant. Following these precautions can lower the risk of neonatal sedation.[7] Numerous professional organizations and regulatory agencies recommend that other agents are preferred over codeine or to avoid codeine completely during breastfeeding;[8][9][10][11][12] however, other opioid alternatives have been studied less and may not be safer.[13]
What should I do if I am breastfeeding mother and I am already exposed to Carisoprodol, Aspirin And Codeine Phosphate Tablet?
We have already established that Carisoprodol, Aspirin And Codeine Phosphate Tablet is unsafe in breastfeeding and breastfeeding while using Carisoprodol, Aspirin And Codeine Phosphate Tablet is not a good idea however if have already used
My health care provider has asked me to use Carisoprodol, Aspirin And Codeine Phosphate Tablet, what to do?
If your doctor knows that you are breastfeeding mother and still prescribes Carisoprodol, Aspirin And Codeine Phosphate Tablet then there must be good reason for that as Carisoprodol, Aspirin And Codeine Phosphate Tablet is considered unsafe, It usually happens when doctor finds that overall advantage of taking
If I am using Carisoprodol, Aspirin And Codeine Phosphate Tablet, will my baby need extra monitoring?
Yes, Extra monitoring is required if mother is using Carisoprodol, Aspirin And Codeine Phosphate Tablet and breastfeeding as it is considered unsafe for baby.
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Carisoprodol, Aspirin And Codeine Phosphate Tablet in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
