
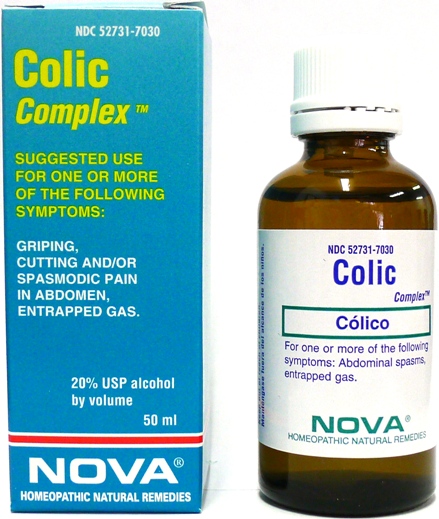
Colic Complex while Breastfeeding
What is Colic Complex used for?
Brief: Suggested use for one or more of the following symptoms: Abdominal spasms, entrapped gas.
Is Colic Complex usage safe while breastfeeding? If a lactating mother is using it can there be any effect on growth or development of infant?

Colic Complex Breastfeeding Analsys
Atropa belladonna while Breastfeeding
UnsafeCAS Number: 8007-93-0
In herbal medicine the leaves of this plant that contains numerous alkaloids are used: l-hyoscyamine and atropine, scopolamine or hyoscine and, all of them potentially high toxic.Traditionally used with poor clinical evidence based on trials as anti-asthmatic, for common colds and intestinal spasms. At latest update no published data on excretion into breast milk were found. With anticholinergic and antimuscarinic properties that may reduce milk production: if necessary take as low dose as possible and avoid long-term treatment if decreasing milk production is observed.Serious side effects (tachycardia, thirst, fever, mydriasis, seizures, coma), especially in infants and newborns (Caksen 2003 Laffargue 2011, Glatstein 2014, Rodríguez-González 2014).There have been cases of gangrene when applied to the chest (Wani 2011). Belladonna may be included in association with other “over the counter" medications of doubtful effectiveness or safety. Overall drug associations are not recommended. Cautions when taking herbal teas:1. Make sure it is obtained from a reliable source: reportedly, poisonings have occurred due to confusion after using another plant with toxic effects (Hsu 1995), some others contain heavy metals that may cause poisoning and others may cause food poisoning due to contamination with bacteria or fungi.2. Do not take it excessively. "Natural" products are not always good in any amount: plants contain active substances from which are made many compounds of our traditional pharmacopoeia that can cause poisoning if consumed in exaggerated quantities or for long periods.
Matricaria recutita while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 520-36-5
It is a widely used plant even in infants. Because of lack of toxicity, a moderate use is considered to be safe. If topically used, do not apply it on the nipple because risk of contact dermatitis has been reported. There are two different species with similar properties: 1) Common or Sweet Chamomile (Matricaria recutita or Chamomilla recutita). 2) Roman, English or Bitter Chamomile (Anthemis nobilis o Chamaemelum nobile). Inflorescence of the herb is used. Contains Essential Oil, Flavonoids, Lactones and Tannins. Unproven properties are: Anti-spasmodic. Digestive, Anti-inflammatory, Sedative.
Citrullus colocynthis fruit pulp while Breastfeeding
DangerousCucurbitaceae plant originally from Turkey with laxative properties. Highly toxic can cause death. Not recommended by the Commission G of the German Ministry of Health. Commercialization of this product has been banned. When present in homeopathic compounds it appears to be harmless.
Lactic acid, dl- while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 50-21-5
A natural product found in milk that may increase their concentration after exercise which is not harmful to the infant. At latest update published were not found data on excretion in breast milk.Because the small dose used and poor absorption to the plasma of most topical dermatological or vaginal preparations, make it unlikely the pass of a significant amount into breast milk. Do not apply on the nipple or areola.
Magnesium phosphate, dibasic trihydrate while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 7757-87-1
Ingested magnesium is not concentrated in the breast milk. Average natural concentration of magnesium in the milk is 31 mg / L (15 to 64 mg / L) which is barely affected by magnesium intake. Its low oral bioavailability makes the step to plasma infant from ingested breast milk is scarce, except in premature and immediate neonatal period that may be characterized by an increased intestinal absorption. Daily Magnesium needs for nursing mothers are estimated at 250 mg.Avoid chronic use or overuse.
Lead while Breastfeeding
UnsafeCAS Number: 7439-92-1
It is an environmental contaminant. As a heavy metal it is found in excess in products like paintings, fuel and metal industry. Certain make-ups, infusion herbals, meat from chased animals and ceramic made pottery may increase the risk of exposure. It can be stored in soft tissues for one month and in bones for decades. Removing of lead from bones occurs during pregnancy and lactation leading to an increase in the serum many years after exposure. It can cause cardiovascular and respiratory toxicity. More intensively it affects infants and children it may cause neurologic damage. Maximal accepted levels by international agencies like WHO, CDC, EFSA – even though a 0 level is desirable – are: 10 mcg/L in water, 5 mcg/L in breast milk and an ingestion of 2.5 mcg/k/d for infants less of 6 months of age. Absorption through the lungs is 50% and through the gut is less than 10%. In blood of unexposed persons serum levels should not be higher than 10 mcg/dL. Working mothers at fertile age showing a lead serum level higher than 30 mcg/dL should be removed from work place. Working pregnant or nursing women should be removed from places with high risk of toxin exposition (Regulated by EU Council Law/85/ from 19.10.1992). Mothers should not breastfeed if they are found to be intoxicated or contaminated. Same recommendation is suitable for mothers who undergo a chelating treatment (since lead is removed from bones and let free). Blood and breast milk testing is highly recommended to have lead level measured. Mothers should avoid nursing whenever lead level is higher than 16 mcg/L in the milk or 16 mcg/dL in the serum. (Lead levels in the milk are usually 10% of those in the serum). Benefits of breastfeeding widely overcome those issues related to the presence of low level environmental contaminants in human milk that in many instances are lower than those present in cow’s milk based products and other food. (Codex alimentarius FAO-WHO). Published papers from studies done on this matter have shown higher lead levels contained in powdered artificial milks than in human milk.
Colic Complex Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
Atropa belladonna while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 8007-93-0
Belladonna (Atropa belladonna) contains anticholinergic alkaloids such as atropine and scopolamine. Belladonna has been used in the past for headache, airway obstruction, and irritable bowel syndrome among others, but its use has been supplanted by more specific and less toxic compounds. Long-term use of belladonna might reduce milk production by reducing serum prolactin.[1] Application of belladonna paste to the nipple to reduce milk secretion during lactation is an extremely old use.[2] However, it is still used this way in rural India for treating breast abscesses and may have contributed to cases of breast gangrene.[3] Because of the narrow therapeutic index and variable potency of plant-based (i.e., nonstandardized) belladonna, it should be avoided orally and topically during lactation. Homeopathic products are not likely to interfere with breastfeeding or cause toxicity. Dietary supplements do not require extensive pre-marketing approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Manufacturers are responsible to ensure the safety, but do not need to the safety and effectiveness of dietary supplements before they are marketed. Dietary supplements may contain multiple ingredients, and differences are often found between labeled and actual ingredients or their amounts. A manufacturer may contract with an independent organization to verify the quality of a product or its ingredients, but that does certify the safety or effectiveness of a product. Because of the above issues, clinical testing results on one product may not be applicable to other products. More detailed information #about dietary supplements# is available elsewhere on the LactMed Web site.
Matricaria recutita while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 8002-66-2
Two different plant species with similar effects are known as chamomile: German chamomile (Matricaria recutita) and Roman chamomile (Chamaemelum nobile). Both contain similar ingredients, including sesquiterpenes (e.g., bisabolol, farnesene), sesquiterpenelactones (e.g., chamazulene, matricin), flavonoids (e.g., apigenin, luteolin), and volatile oils. Chamomile is used orally as a sedative and for gastrointestinal conditions; it is used topically for wound healing. Both herbal and homeopathic preparations have been used to treat mastitis and cracked, bleeding nipples.[1] Chamomile has been used as a galactogogue;[2][3] however, no scientifically valid clinical trials support this use. Galactogogues should never replace evaluation and counseling on modifiable factors that affect milk production.[4] Chamomile is "generally recognized as safe" (GRAS) for use in food by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a spice, seasoning, or flavoring agent. No data exist on the safety of chamomile in nursing mothers or infants, although rare sensitization may occur (see below).[5] It has been safely and effectively used alone and with other herbs in infants for the treatment of colic, diarrhea, and other conditions,[6][7][8][9] so the smaller amounts expected (but not demonstrated) in breastmilk are likely not to be harmful with usual maternal doses. Note Clostridium botulinum (botulism) spores have been found in some loose-leaf chamomile teas sold in health food stores. Topical chamomile is a known sensitizing agent, even with homeopathic products.[10] Two women developed contact dermatitis of the nipples and areolas after applying Kamillosan ointment for cracked nipples. The product was purchased in England and contained 10.5% Roman chamomile extracts and oil. Reactions were confirmed to be caused by Roman chamomile by patch testing in both women. Drinking chamomile tea can exacerbate topical skin rashes and has caused anaphylaxis in sensitized individuals.[11] Chamomile has possible cross-reactivity with other members of the aster family (e.g., echinacea, feverfew, and milk thistle).[5] Dietary supplements do not require extensive pre-marketing approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Manufacturers are responsible to ensure the safety, but do not need to the safety and effectiveness of dietary supplements before they are marketed. Dietary supplements may contain multiple ingredients, and differences are often found between labeled and actual ingredients or their amounts. A manufacturer may contract with an independent organization to verify the quality of a product or its ingredients, but that does certify the safety or effectiveness of a product. Because of the above issues, clinical testing results on one product may not be applicable to other products. More detailed information #about dietary supplements# is available elsewhere on the LactMed Web site.
What should I do if already breastfed my kid after using Colic Complex?
Due to high dilution of ingredients in homeopathic medicines they do not create much problem for baby. Colic Complex is a homeopathic medicine and if your baby does not have any abnormal symptoms then there is nothing to worry about. Be careful with too much usage of ethanol based homeopathic medicines during breastfeeding.
I am nursing mother and my doctor has suggested me to use Colic Complex, is it safe?
Homeopathic medicines are usually safe in breastfeeding and if Colic Complex has been recommended by doctor then there should be no concern about its usage in breastfeeding.
If I am using Colic Complex, will my baby need extra monitoring?
Not exactly.
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Colic Complex in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
