Insomulex Insomnia Symptom Relief while Breastfeeding
What is Insomulex Insomnia Symptom Relief used for?
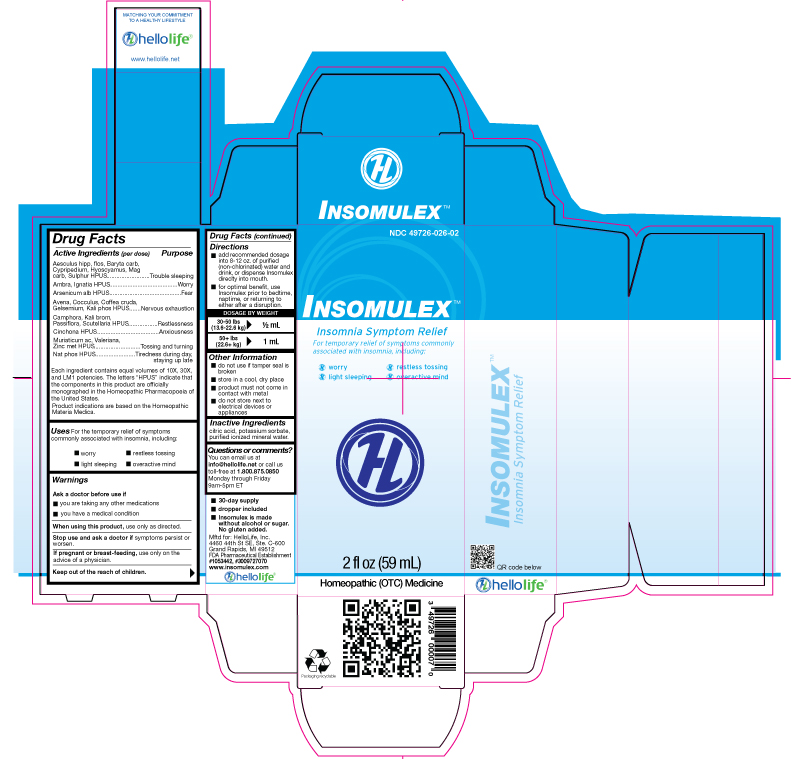
Purpose: Aesculus hipp, flos, Baryta carb, Cypripedium, Hyoscyamus, Mag carb, Sulphur HPUS.....................................Trouble sleeping Ambra, Ignatia HPUS...................................................................................................................................................Worry Arsenicum alb HPUS....................................................................................................................................................Fear Avena, Cocculus, Coffea cruda, Gelsemium, Kali phos HPUS....................................................................Nervous Exhaustion Camphora, Kali brom, Passiflora, Scutellaria HPUS.............................................................................................Restlessness Cinchona HPUS................................................................................................................................................Anxiousness Muriaticum ac, Valeriana, Zinc met HPUS.................................................................................................Tossing and Turning Nat phos HPUS..............................................................................................................Tiredness during day, staying up late Each ingredient contains equal volumes of 10X, 30X, and LM1 potencies. The letters “HPUS” indicate that the components in this product are officially monographed in the Homeopathic Pharmacopoeia of the United States. Indications are based on Homeopathic Materia Medica.
Insomulex Insomnia Symptom Relief while breastfeeding safe or not? Can there be any side effects for infant while using it during breastfeeding?

Insomulex Insomnia Symptom Relief Breastfeeding Analsys
Avena sativa flowering top while Breastfeeding
SafeThe seeds of this leguminous plant are used. Content: carbohydrates, proteins, saponins, vitamins, minerals . Assigned properties: appetite stimulant, lowering of lipemia and glycemic (Gong 2016).Indications according to Commission E of the German Ministry of Health: Anorexia, Atopic Dermatitis. Widely used as a galactogogue in many cultures around the world (Ayers 2000, Winterfeld 2012, Sim 2013, The Royal Women's .. 2013, Bazzano 2016). Case-control studies looking for evidence on the increment of milk production associated to the use of fenugreek are few (Turkyılmaz 2011, Ghasemi 2015), along with a variety of methodological deficiencies. Other studies have failed to find such an effect with the use of fenugreek (Damanik 2006). Studies with an appropriate design are needed to provide high quality evidence to make clinical recommendations on its use (Forinash 2012, Zapantis 2012, Committee LM AEP 2012, Mortel 2013, Bazzano 2016) A higher antioxidant effect in the breastmilk of women who have consumed mixed infusions containing this or other herbs has not been shown (Kavurt 2013). Given the wide spread use and lack of toxicity of this herb, a moderate consumption would be compatible with breastfeeding, yet high doses may produce hypoglycemia (EMA 2011, Gong 2016) and, because of the odor appearing in the urine of the infant, a lab test may be required to make a differential diagnosis with maple syrup disease of the newborn (Sewell 1999, Korman 2001). Avoid the use of a galactogogue without a sanitary control. Best galactagogue results are achieved through on-demand breastfeeding along with an adequate technique in a mother who is able to maintain self-confidence (ABM 2011, Mannion 2012). Precautions when taking plant preparations: 1. Ensure that they are from a reliable source: poisoning has occurred due to confusing one plant with another with toxic properties, as well as poisoning from heavy metals extracted from the ground and food poisoning due to contamination with bacteria or fungi. 2. Do not take in large amounts; follow recommendations from professional experts in phytotherapy. "Natural" products are not always good in any quantity: plants contain active substances from which much of our traditional pharmacopoeia has been obtained and can result in poisoning or act as endocrine disruptors if taken in excessive amounts or time periods.
Camphor (natural) while Breastfeeding
UnsafeCAS Number: 76-22-2
Substance which can be extracted under distillation from the Camphor tree bark. Nowadays it is synthesized from the Turpentine. Used with creams and lotions as local anti-inflammatory agent. There is no proof of effectiveness as decongestant or expectorant when used in inhaled preparations, but as a toxic agent. Camphor is a highly lipophilic substance which is well absorbed by whatever via of administration (skin, inhalation, mouth) that crosses easily the cell membrane. Pharmacokinetic data support the likelihood of excretion into breast milk in a significant amount. Camphor has been shown to be toxic at low dose on infants in whom it may cause headache, vomiting, seizures and coma. It should never be administered by mouth. It is not appropriate its use during breastfeeding, and, in whatever case, it should not be applied on the mother's breast, since severe intoxications be occurred in infants after use of small ingested amounts. Be aware of not using it in the nostrils.
Cinchona officinalis bark while Breastfeeding
SafeCinchona alkaloid used in the prophylaxis and treatment of malaria (Pérez 2009). Administered orally or intravenously. It is excreted in breast milk in clinically insignificant amounts (Mathew 2004, Phillips 1986, Terwilliger 1934), much lower than the dose used in newborns and infants (Fulton 1992).No problems have been observed in infants whose mothers were taking it (FDA 2008, Terwilliger 1934). Its use is authorized in infants and children.Avoid in cases of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (Mathew 2004, WHO/UNICEF 2002, Fulton 1992). American Academy of Pediatrics: medication usually compatible with breastfeeding (AAP 2001). WHO list of essential medicines: compatible with breastfeeding (WHO / UNICEF, 2002).
Arabica coffee bean while Breastfeeding
Low RiskCAS Number: 84650-00-0
Infant intake after usual daily consumption of the mother is lower than usual recommended dose for neonatal apnea treatment. Elimination-time period may last from few hours in adults, to 3-4 days in the newborn infant. At higher dose (more than 300 mg per day) caffeine may induce irritability, tremor and insomnia in the infant. However, some infants may develop irritability at a lower dose; in those cases the mother should decide appropriate coffee intake. Some studies have failed to show harmful effect among infants whose mothers were strong coffee consumers even during pregnancy. Daily intake as high as 1 liter or more has been associated to anemia and iron deficiency in mothers and breastfed infants. Also, has been related to the Raynaud's phenomenon in the nipple of nursing women. Mean Caffeine content: 1 coffee cup: 100 mg, 1 black tea cup: 80 mg, 1 green tea cup: 50 mg, 1 liter of cola & soda and energizers beverages 100 to 340 mg. See also Caffeine as medication. The American Academy of Pediatrics rates it compatible with breastfeeding.
Strychnos ignatii seed while Breastfeeding
DangerousCAS Number: 8046-97-7
Dried seed of this plant has been used. It contains brucine and strychnine. It is highly toxic and easily lethal.
Potassium bromide while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 7447-40-7
Human milk has a potassium concentration of 13 meq/L, almost a half of rehydration solution content and a quarter of maximal IV recommended dose. Potassium supplementation does not alter milk concentration without increasing mother’s serum concentration, which is strictly limited from 3,5 to 5,5 meq/L.
Potassium phosphate, dibasic while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 7447-40-7
Human milk has a potassium concentration of 13 meq/L, almost a half of rehydration solution content and a quarter of maximal IV recommended dose. Potassium supplementation does not alter milk concentration without increasing mother’s serum concentration, which is strictly limited from 3,5 to 5,5 meq/L.
Magnesium carbonate while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 546-93-0
Ingested Magnesium does not concentrate into breast milk. Naturally occurring, the mean Magnesium concentration in the milk is 31 mg/L (range 15 – 64 mg/L) and not affected by the ingestion of Magnesium. Because of a low oral bioavailability the pass from the breast milk toward the infant's plasma is hampered, except in premature and newborn infants who may exhibit a higher intestinal absorption due to an increased permeability. Avoid chronic or excessive use. WHO Model List of Essential Medicines 2002: Magnesium carbonate is compatible with breastfeeding.
Passiflora incarnata flowering top while Breastfeeding
Low RiskCAS Number: 8057-62-3
At latest update, relevant information on excretion into breast milk was not found. Aerial summits of this climbing plant are used. Constituents are: flavonoids, pyranics, heterosides, alkaloids. Attributed effects with only weak scientific evidence on effectiveness are: sedative, hypnotic, anti-spasmodic. Because of paucity of data on toxicity, recommendations done are to use it at low doses for short term periods. The European Medicines Agency does not authorize its use for children younger than 12 years old , pregnancy and breastfeeding. When used while breastfeeding, it is recommended to use it at low dose for a short-term period. Following-up the infant for sedation is recommended.
Arsenic trioxide while Breastfeeding
DangerousUsed in the treatment of promyelocitic leukemia in adults.
Valerian while Breastfeeding
Low RiskCAS Number: 8057-49-6
At last update significant data on breastfeeding were not found. A commonly used herb in many cultures and countries, even during pregnancy and breastfeeding with very few reported side-effects. Whenever not abused it has a low toxicity. Moderate use is considered to be compatible with breastfeeding, however because of the possibility of sedative effect in infants should better be avoided in cases of prematurity and in the neonatal period. Be aware of sedative effects in the infant. Roots, rhizomes and stolons of the plant are used. It contains iridoids, valepotriates, steroids, essential oils, GABA and tannins. Unproven beneficial effects in adults: sedative, hypnotic, anti-spasmodic. Indication after Commission E of German Ministry of Health: insomnia, nervousness, anxiety. Maximal daily dose: 9 g (2 g of dried extract)
Zinc while Breastfeeding
SafeZinc (Zn) is an essential element for nutrition. It is present in many foods.Recommended daily allowance of Zn is 8 to 15 mg. (Moran Hall 2010). Millions of people worldwide are Zn-deficient.It is used as a treatment for Wilson's disease and Acrodermatitis Enteropathica. Zn is involved in the regulation process of lactation (Lee 2016).Pasteurization of the milk does not affect the concentration of Zn and other trace elements (Mohd Taufek-2016). The average concentration of Zn in breastmilk is 4 to 16 mg / L (Picciano 1976, Hannan 2005, Dórea 2012) which is independent of plasma levels and maternal daily intake (Krebs 1995, Chierici 1999, Hannan 2009).Intestinal absorption of zinc is almost doubled during pregnancy and lactation (Fung 1997).Zinc levels in the infant are dependent on Zinc levels in the breast milk (Dumrongwongsiri 2015)With a varied and balanced diet, an extra intake of minerals is not needed. Excessive intake of Zinc may cause gastrointestinal problems and Pancytopenia (Irving 2003).
Insomulex Insomnia Symptom Relief Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
Barium carbonate while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 7727-43-7
Because barium sulfate is not absorbed after oral or rectal administration, it will not enter the milk, reach the bloodstream of the infant or cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. No special precautions are required.
Cinchona officinalis bark while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 130-95-0
Because of the low levels of quinine in breastmilk, amounts ingested by the infant are small and would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. The dosage in milk is far below those required to treat an infant for malaria.[1] However, quinine should not be used in mothers with an infant who is glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficient.[2] Even the relatively small amounts of quinine in tonic water ingested by the mother have caused hemolysis in G6PD-deficient infants.
Sodium phosphate, dibasic, heptahydrate while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 7558-79-4; 7558-80-7
Phosphate is a normal constituent of breastmilk. Phosphate concentrations have not been measured in breastmilk after large maternal doses of sodium phosphate, such a 30 gram oral dose for pre-procedural bowel evacuation. However, the added phosphate in breastmilk is likely to be only about 130 mg over 24 hours in this situation. The increase from a typical dose of a rectal enema would be considerably less than this amount. Breastmilk sodium concentration is tightly regulated, and will not be affected. It is probably not necessary to suspend breastfeeding after the use of oral sodium phosphate solutions given once or twice for bowel evacuation before a procedure, but if there is concern, suspension of nursing for 24 hours after a dose should result in negligible increase in phosphate ingestion by the infant. Use of a phosphate rectal enema by a nursing mother would require no special precautions.
Arsenic trioxide while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 1327-53-3
Most sources consider breastfeeding to be contraindicated during maternal antineoplastic drug therapy. It might be possible to breastfeed safely during intermittent therapy with an appropriate period of breastfeeding abstinence; the manufacturer recommends an abstinence period of 1 week after the last dose. Chemotherapy may adversely affect the normal microbiome and chemical makeup of breastmilk.[1] Women who receive chemotherapy during pregnancy are more likely to have difficulty nursing their infant.[2]
Sulfur while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 7704-34-9
Sulfur 5% to 10% in a petrolatum base is safe for topical use in children, including infants under 2 months of age.[1] This makes it a useful alternative to organic insecticides for treating scabies in nursing mothers; however, the petrolatum base makes undesirable for use on the breast.
Valerian while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 8008-88-6; 8057-49-6
Valerian (Valeriana officinalis) root contains mono- and sesquiterpenes, and iridoid triesters (valepotriates). Preparations are sometimes standardized on valerenic acid content. Valerian has no specific uses in nursing mothers, but is most commonly used to treat anxiety and sleep disturbances, and occasionally for self-treatment of postpartum blues or depression.[1][2] No data exist on the safety and efficacy of valerian in nursing mothers or infants. In general, valerian is well tolerated, with side effects such as dizziness, hangover or headache reported occasionally. Valerian is "generally recognized as safe" (GRAS) for use in food by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Valerian is often not recommended during lactation because of the theoretical concerns over its valepotriates and baldrinals which have been shown to be cytotoxic and mutagenic in vitro. Because there is no published experience with valerian during breastfeeding, an alternate therapy may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. Dietary supplements do not require extensive pre-marketing approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Manufacturers are responsible to ensure the safety, but do not need to the safety and effectiveness of dietary supplements before they are marketed. Dietary supplements may contain multiple ingredients, and differences are often found between labeled and actual ingredients or their amounts. A manufacturer may contract with an independent organization to verify the quality of a product or its ingredients, but that does certify the safety or effectiveness of a product. Because of the above issues, clinical testing results on one product may not be applicable to other products. More detailed information #about dietary supplements# is available elsewhere on the LactMed Web site.
Insomulex Insomnia Symptom Relief Breastfeeding Analsys - 3
Gelsemium sempervirens root and Breastfeeding
UnsafeAll parts of the false jasmine usually contain toxic alkaloids. Eating just one flower has reportedly been lethal to children. The plant can also cause skin allergies in some people and it is possible that the plant toxins can be absorbed through the skin, especially if there are cuts. It�s not recommended to use false jasmine while breastfeeding. It is acceptable in homeopathic preparation.
Sodium phosphate, dibasic, heptahydrate and Breastfeeding
SafeSulfur and Breastfeeding
SafeNote: Study and data for tropical use only
Warning: Tropical usage in breast area shall be avoided to prevent the Thuja passing orally in Infants.
What should I do if I am breastfeeding mother and I am already exposed to Insomulex Insomnia Symptom Relief?
Due to high dilution of ingredients in homeopathic medicines they do not create much problem for baby. Insomulex Insomnia Symptom Relief is a homeopathic medicine and if your baby does not have any abnormal symptoms then there is nothing to worry about. Be careful with too much usage of ethanol based homeopathic medicines during breastfeeding.
I am nursing mother and my doctor has suggested me to use Insomulex Insomnia Symptom Relief, is it safe?
Homeopathic medicines are usually safe in breastfeeding and if Insomulex Insomnia Symptom Relief has been recommended by doctor then there should be no concern about its usage in breastfeeding.
If I am using Insomulex Insomnia Symptom Relief, will my baby need extra monitoring?
Not exactly.
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Insomulex Insomnia Symptom Relief in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
