Sulfamethoxazole And Trimethoprim Tablet while Breastfeeding
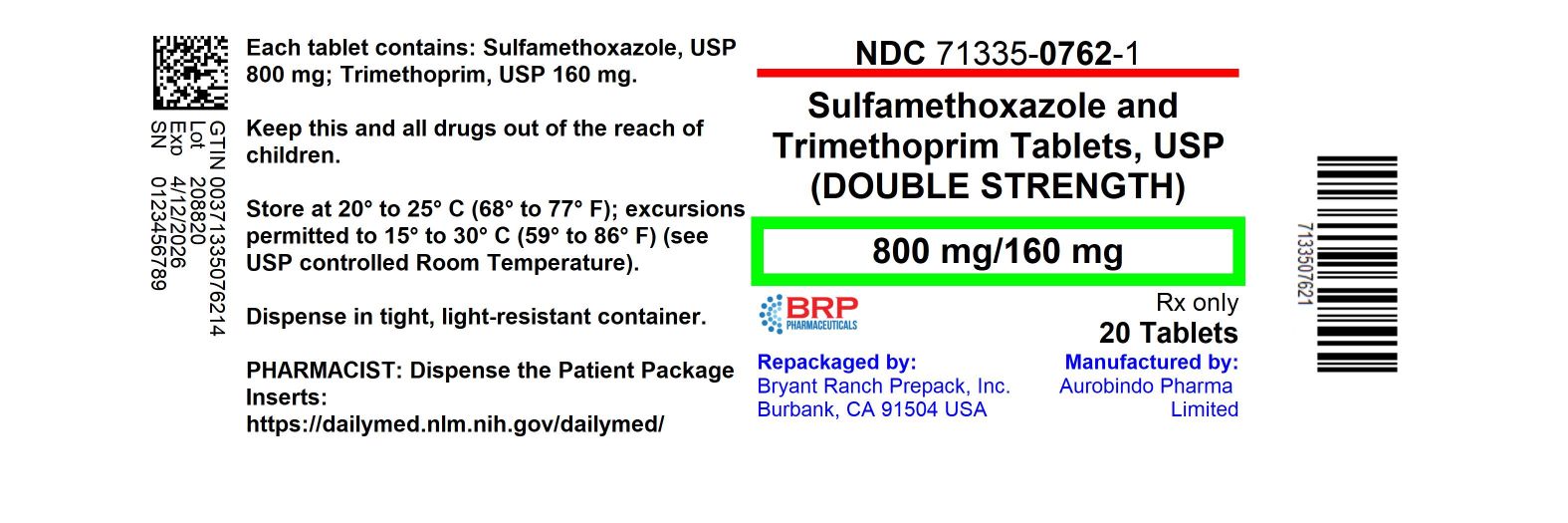
What is Sulfamethoxazole And Trimethoprim Tablet used for?
What are the risk associated with Sulfamethoxazole And Trimethoprim Tablet usage while breastfeeding? What precautions shall I take while using it in breastfeeding?

Nursing Mothers Levels of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole in breast milk are approximately 2 to 5% of the recommended daily dose for infants over 2 months of age. Caution should be exercised when sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is administered to a nursing woman, especially when breastfeeding, jaundiced, ill, stressed, or premature infants because of the potential risk of bilirubin displacement and kernicterus.
Sulfamethoxazole And Trimethoprim Tablet Breastfeeding Analsys
Sulfamethoxazole while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 723-46-6
Excreted in non-significant levels into breast milk. No adverse effects have been shown in breastfed infants. Caution with those neonates suffering of hyperbilirrubinemia or G-6-P-D deficiency is required. Avoid use in affected patients Check-up for infant jaundice. Be aware of false negative results of bacterial cultures when the mother is on antibiotics. American Academy of Pediatrics: Maternal Medication Usually Compatible With Breastfeeding.Eleventh WHO Model List of Essential Drugs 2002: Compatible with breastfeeding.
Trimethoprim while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 738-70-5
It is excreted in breast milk in clinically non-significant amount. No problems have been observed in infants whose mothers were treated. Medication which is used in infants from the second month of age. Take into account the possibility of negative false results of cultures from febrile infants whose mothers are taking antibiotics as well as the possibility of acute diarrhea due to imbalance of the intestinal flora. The American Academy of Pediatric states that it is usually compatible with breastfeeding medication.WHO List of Essential Medicines from 2002 has classified it as compatible with breastfeeding.
Sulfamethoxazole And Trimethoprim Tablet Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
Sulfamethoxazole while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 723-46-6
With healthy, fullterm infants it appears acceptable to use sulfamethoxazole during breastfeeding after the newborn period. The time of greatest risk for hemolysis in fullterm newborns without glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency might be as short as 8 days after birth.[1] Until further data are accumulated, alternate agents should probably be used in jaundiced, ill, stressed or premature infants, because of the risk of bilirubin displacement and kernicterus. Sulfamethoxazole should be avoided while breastfeeding a G6PD deficient infant.[2]
Trimethoprim while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 738-70-5
Because of the low levels of trimethoprim in breastmilk, amounts ingested by the infant are small and would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants.
What should I do if I am breastfeeding mother and I am already exposed to Sulfamethoxazole And Trimethoprim Tablet?
As usage of Sulfamethoxazole And Trimethoprim Tablet is mostly safe while breastfeeding hence there should not be any concern. In case of any change in behavior or health of your baby you should inform your health care provider about usage of Sulfamethoxazole And Trimethoprim Tablet else no further action is required.
I am nursing mother and my doctor has suggested me to use Sulfamethoxazole And Trimethoprim Tablet, is it safe?
Definitely, Sulfamethoxazole And Trimethoprim Tablet is safe in lactation for baby. No wonder your doctor has recommended it.
If I am using Sulfamethoxazole And Trimethoprim Tablet, will my baby need extra monitoring?
No extra baby monitoring required while mother is using Sulfamethoxazole And Trimethoprim Tablet
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Sulfamethoxazole And Trimethoprim Tablet in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
